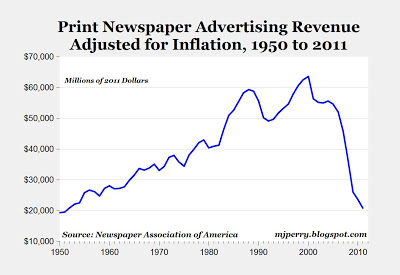
The Collapse of Print Advertising in 1 Graph
Call it creative if you want, but this is what economic destruction looks like. Print newspaper ads have fallen by two-thirds from $60 billion in the late-1990s to $20 billion in 2011.
You sometimes hear it said that newspapers are dead. Now, $20 billion is the kind of "dead" most people would trade their lives for. You never hear anybody say "bars and nightclubs are dead!" when in fact that industry's current revenue amounts to an identical $20 billion.
So the reason newspapers are in trouble isn't that they aren't making lots of money -- they still are; advertising is a huge, huge business, as any app developer will try to tell you -- but that their business models and payroll depend on so much more money. The U.S. newspaper industry was built to support $50 billion to $60 billion in total advertising with the kind of staffs that a $50 billion industry can abide. The layoffs, buyouts, and bankruptcies you hear about are the result of this massive correction in the face of falling revenue. The Internet took out print's knees in the last decade -- not all print*, but a lot.
Don't just blame the bloggers. For decades, newspapers relied on a simple cross-subsidy to pay for their coverage. You can't make much money advertising against A1 stories like bombings in Afghanistan and school shootings and deficit reduction. Those stories are the door through which readers walk to find stories that can take the ads: the car section, the style section, the travel section, and the classifieds. But ad dollars started flowing to websites that gave people their car, style, travel, or classifieds directly. So did the readers. And down went print.
The decline is stunning. "Last year's ad revenues of about $21 billion were less than half of the $46 billion spent just four years ago in 2007, and less than one-third of the $64 billion spent in 2000," Mark Perry writes. In the next few years -- and hopefully, in the next few decades (I like print!) -- we'll see papers and magazines continue to invest in their websites and find advertising and pricing models that support journalism independently. Otherwise, one hopes that rich people continue to be fond of paying for the production of great writing on bundles of ink and paper.
_________________
*This graph is a useful reminder of the comparative performance of the nation's biggest newspapers.